Color by Design
- Visible Spectrum:
- The band of colors produced when white light passes through a prism or raindrops.
- Pigment:
- The dry natural minerals or synthetic chemicals used to color the basic neutral paint medium.
- Palette:
- The resultant partnering of colors designed to form a cohesive group.
Color in Itself
- Color Wheel:
- ‘Rainbow’ color segments placed in a circle positioning the relationships between and amongst colors.
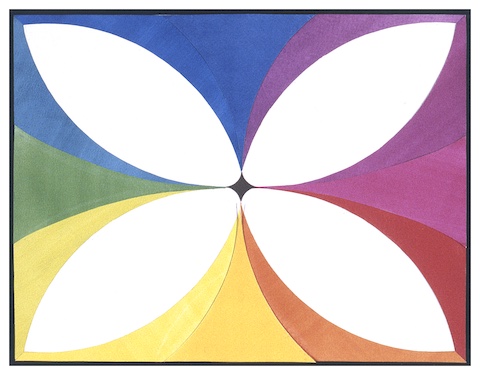

- Hue:
- The name of each specific pure color on a color wheel e.g., yellow, green, blue, violet, red, orange.
Color in Relationship to Color
- Primary Colors:
- In paint, the hues red, yellow & blue that cannot be produced by mixing any other pigment.


- Secondary Colors:
- In paint, the hues orange, green & violet that are created when primary pigments are intermixed.


- Analogous Colors:
- Hues lying adjacent to one another on a classic color
wheel: red, orange & yellow; yellow, green & blue; blue, violet &
red.
- Warm Colors:
- red, orange & yellow.

- Cool Colors:
- green, blue & violet.

- Complementary Colors:
- A pair of hues comprised of one Primary
and one Secondary positioned across from one another on a color wheel:
yellow & violet; orange & blue; red & green.


- Earth Colors:
- Neutral, muted hues created by mixing any pair of complementary colors.


- Full Spectrum Colors:
- Hues mixed without using black or white pigments.
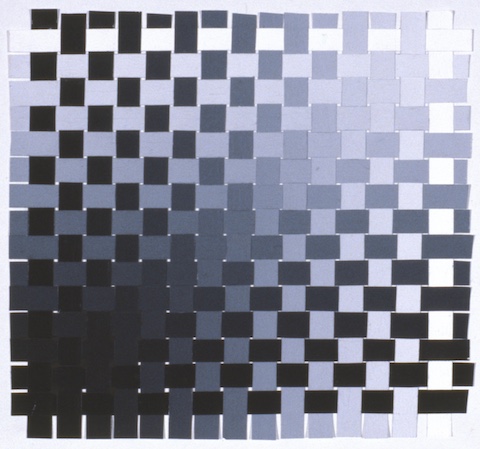
- Value:
- The lightness or darkness of each hue and its relative position on a scale from white to black.
- Tints:
- Hues lightened by the gradual addition of white.

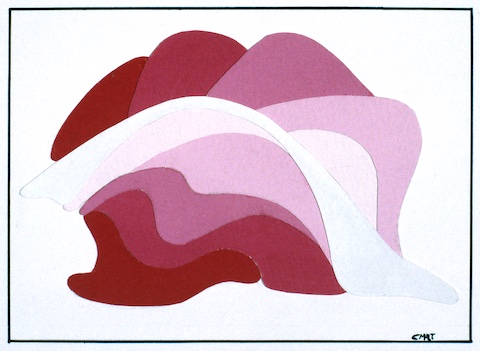
- Shades:
- Hues darkened by the gradual addition of black.


- Tones:
- Hues changed by the gradual addition of grey.


Color's Personality…
A Conspiracy of Illusion and Deception
- Local Color:
- The isolated natural color of a thing in itself, independent of and uninfluenced by adjacent things.
- Perceiving or "Reading" Color
- is dependent upon:
- Light Source
-
- Direct or diffuse NATURAL LIGHT as effected by cast and reflected shadow.
- ARTIFICIAL LIGHT e.g., incandescent, LED, florescent, halogen, etc…
- Adjacent Colors
- actively reflect and/or absorb one another.
- Full intensity complementary colors placed adjacent to one another tend to bounce or vibrate.
- Mismatched colors placed next to one another tend to absorb and dull one another.
- Saturation:
- Refers to the intensity of each color.
- High intensity
-

- Low intensity
-

- Contrast:
- Differences in intensity.
- High contrast:
- Extreme differences between colors.


- Low contrast:
- Greater similarity of colors one to another.


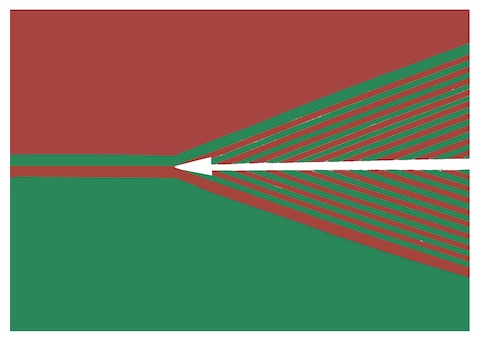
- Cool, Shaded Hues:
- appear to RECEDE.
- Warm, Tinted Hues:
- appear to ADVANCE.
 Squint your eyes to make the illusion work.
Squint your eyes to make the illusion work.