Formal Visual Elements
Familiarity with the words of the trade and understanding their meanings will help
- Facilitate our communication,
- Convey how you envision your project, and
- Enhance my understanding of what you imagine.
2-Dimensional Visual Elements
- 2-Dimensional
- pertains to marks on a surface and to the illusions
created by those marks.
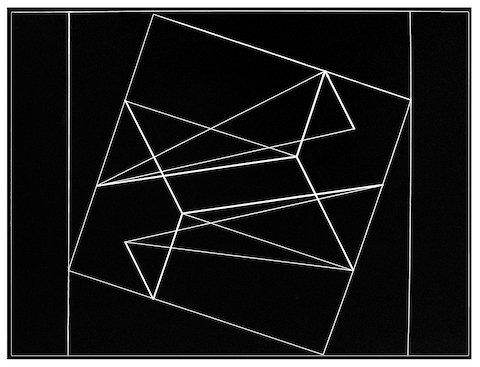
- Character:
- The particular quality of or relationship between elements;
the resultant impression of personality, feeling, or sense of spirit.


- Line:
- A long narrow mark.
- positive:
- Where the line is.
- negative:
- Where the line isn't.
- Path:
- The character of a line described from one end to the other.
- straight, angular, zig-zag
-

- curved, lyrical, wavy
-

- Shape:
- An enclosed area that is caught and defined when the head
of a line meets its tail.


- Negative Shape (aka Volume):
- The area of lesser saturation, or lighter illusory weight; where the color isn't.

- Positive Shape (aka Mass):
- The area of greater saturation, or heavier illusory weight; where the color is.


- (Implied) Texture:
- The impression or illusion of tactile qualities.

3-Dimensional Visual Elements
- 3-Dimensional
- pertains to the actual, physically perceptible
qualities of solid material.

- Character:
- The particular quality of or relationship between
things; the resultant impression of personality, feeling, or sense of spirit.


- Line:
- The illusion discerned when materials of differing
character abut one another.



- Space:
-
- The unimpeded area contained within physical barriers.

- The vacant area surrounding material objects.

- The unimpeded area contained within physical barriers.
- Shape:
- The quality or resultant character of mass placed in space.
- angular
-


- curved
-


- Mass:
- The material bulk of the physical objects that interfere
with, divide, or inhabit space.


- Volume:
- The space devoid of material.


- (Actual) Texture:
- The actual tactile qualities on material surfaces.
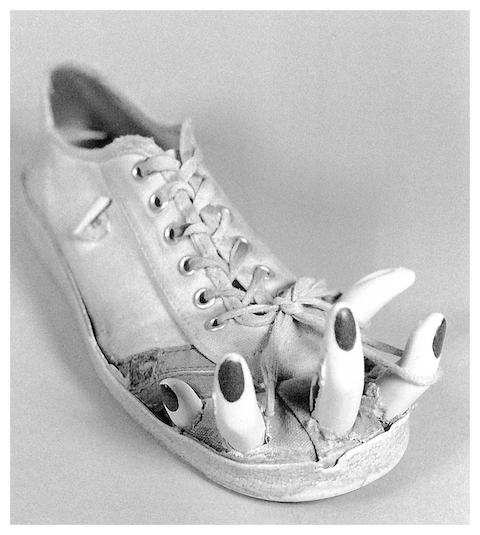



Design Principles
- The Design Principles
- arrange the CHARACTER or quality of relationships between Visual Elements.



- Scale:
- The relative size of shapes or objects to one another; the
relationship of those to the viewer.


- Proportion:
- The size relationship of parts to one another or of
parts to the whole.


- Weight:
- Material substance, bulk; gravity.
- [Illusion of] Mass:
-


- [Illusion of] Volume:
-


- Balance:
- The illusion of weight or force.
- Bi-Symmetry:
- Shapes or objects evenly placed across a central axis.
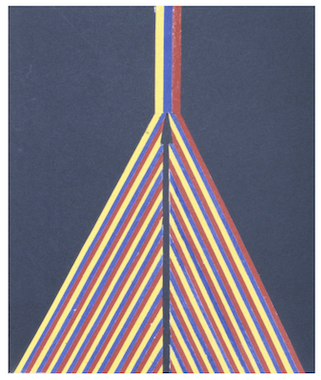

- Radial Symmetry:
- Shapes or objects extending out from an
obvious centrally located point.


- Asymmetry:
- Lopsided, uneven placement or grouping of shapes or objects.


- Repetition creates Rhythm:
- The organization and recurrence of elements.








- Variety with Unity:
- The diversity and integration of elements.


- Harmony:
- The pleasing employment of elements


- Dis-harmony:
- Visual confusion.

